The Search Phase: Creating Customer Value
.png)
1. Customer-Problem Fit:
The first step in the search phase involves idea validation. The startup focuses on formulating a problem hypothesis statement and identifying potential early customers. Through conversations with these customers, the founding team aims to gain insights into their problems and challenges. Analyzing these interviews helps determine which problem presents a viable market opportunity. It's worth mentioning that disproving a hypothesis at this stage can lead to the discovery of a better idea.
2. Problem-Solution Fit:
Once a problem has been identified, the startup moves on to developing a feasible solution. This solution should be something that the team can create with the available resources. The Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is a popular term used to describe the solution built during this phase. The MVP should encompass the essential features that showcase the startup's value proposition.
3. Customer-Solution Fit:
In this phase, the startup tests the MVP with early adopters to gauge their willingness to use it. The founding team should be open to experimenting with different versions of the MVP and iterating based on user feedback. The objective is to arrive at a usable solution that aligns with the customers' needs and preferences.
The Execute Phase: Creating Business Value
.png)
1. Product-Channel Fit:
During this phase, the startup explores different distribution channels and conducts tests to identify the most effective one. If a significant portion of the startup's growth comes from a particular channel, it indicates that the product-channel fit has been achieved. This fit ensures that the product reaches the right customers through the most suitable channels.
2. Channel-Model Fit:
It is essential to understand that not every business model thrives in every channel. This phase requires rigorous iterations, particularly in terms of pricing models, to ensure their effectiveness and alignment with the chosen channels. Finding the right fit between the channel and the business model is crucial for sustainable growth.
When the team is able to fold its business model to fit the needs of at least one distribution channel, then that team is said to have achieved channel-model fit.
The relationship between (Average Revenue Per User) ARPU and CAC (Customer Acquisition Cost) are important determinants of the Channel-Model Fit. What plays an important role in ARPU is the pricing model of the startup. During this phase, startups should gather feedback and data from their customers, closely monitor competitors' pricing strategies, and conduct market research to understand customers' willingness to pay. This information serves as a foundation for making informed decisions and refining the pricing model to achieve maximum profitability and customer satisfaction.
Ultimately, finding the right channel-model fit sets the stage for sustainable growth. By aligning their business model with the most effective distribution channel and optimizing their pricing strategy, startups can establish a strong foundation for success and maximize their potential for long-term viability in the market.
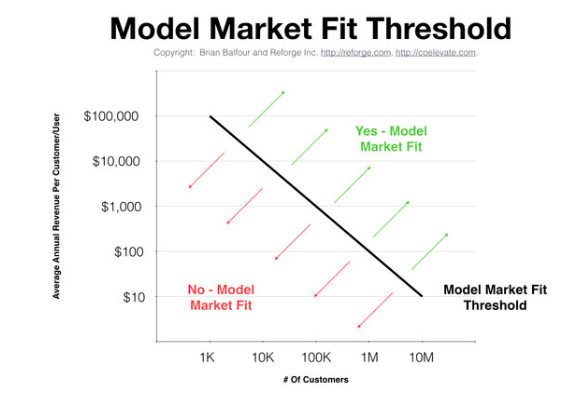
3. Model-Market Fit:
This phase highlights the influence of the market on the startup's model. The number of potential customers within the market and the percentage of those customers that the startup has captured play a significant role in determining the extent to which the startup will achieve model-market fit. Christoph Janz of Point Nine Capital provides an inspiring approach to defining the market with "The Five Ways to Build a $100M Business." Additionally, Brian Balfour, the former VP of Growth at HubSpot, successfully demonstrates model-market fit through the area above the Average Revenue Per User (ARPU) versus the number of customers graph.
4. Product-Market Fit:
The ultimate proof of a startup's viable business model and readiness to scale is achieved through product-market fit. When a startup begins to experience double-digit revenue growth numbers, it signifies that product-market fit has been attained. This phase is a crucial milestone that validates the startup's value proposition and paves the way for sustainable expansion.
Achieving product-market fit signifies that the startup has found a sweet spot where their offering resonates with customers, leading to accelerated growth and market success.
Iterative development and continuous improvement are key factors in achieving product-market fit. Startups must be adaptable and willing to make necessary adjustments based on customer feedback. This iterative process allows them to refine their offering, address any shortcomings, and enhance the value proposition for customers.
Product-market fit is not a one-time accomplishment but an ongoing pursuit. As the market evolves and customer needs change, startups must stay vigilant and adapt their offering to maintain alignment with the market. Continuous market analysis, customer engagement, and product enhancements are crucial to sustain and build upon the achieved product-market fit.