In the world of startups, scaleups, and corporate innovation, strategy is meaningless without execution. Many ambitious entrepreneurs and professionals craft compelling visions but struggle to turn them into tangible progress. The Cascade Model offers a practical and structured framework that helps break down grand strategies into actionable steps. This article explores how the model works and how you can apply it to stay focused, aligned, and results-driven.
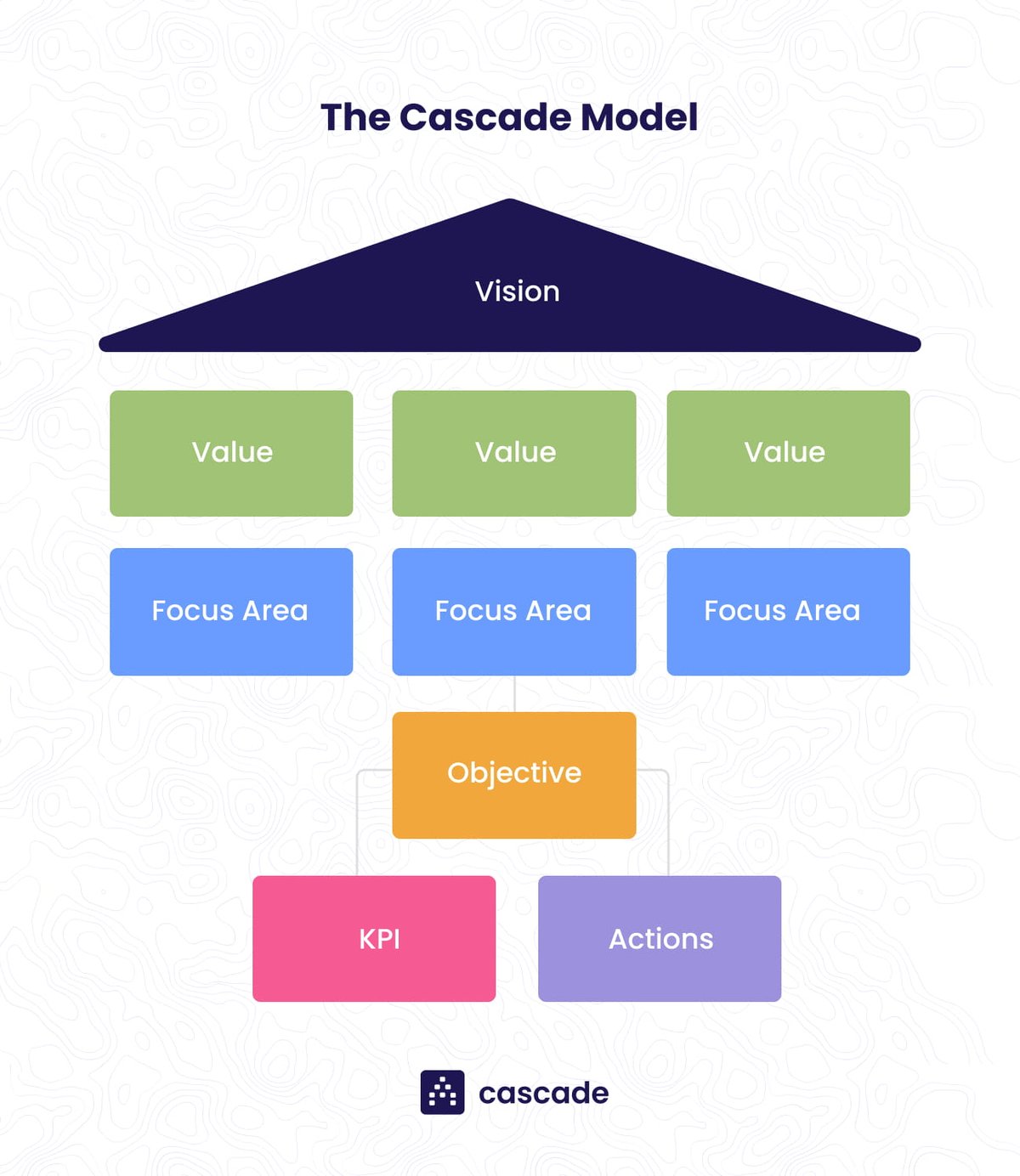
What is the Cascade Model?
The Cascade Model is a strategic planning framework that connects high-level vision to daily execution. It breaks down strategy into six interconnected layers:
- Vision
- Values
- Focus Areas
- Objectives
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
- Actions
By working through these layers in sequence, you create a clear line of sight from long-term goals to the day-to-day tasks that move you forward. It’s a popular method for teams that need clarity, alignment, and agility—especially in fast-changing environments.
Source: Cascade Blog – Strategy Planning Models
1. Start with Your Vision
A vision is your strategic north star. It captures what you ultimately want to achieve and defines your ideal future. It should be ambitious yet grounded, specific enough to guide decision-making but flexible enough to adapt as needed.
Examples of strong visions include:
- "Become the leading platform for remote education in developing countries."
- "Transform how small businesses access financial tools."
Your vision should be easy to remember, emotionally resonant, and directionally clear. A strong vision not only motivates internally but also helps communicate externally what your organization stands for.
To craft a powerful vision, ask yourself:
- What impact do we want to have?
- Who do we serve, and how will their world change?
- What will success look like 5–10 years from now?
A good vision is both a rallying cry and a filter for decision-making.
2. Define Your Values
Values define how you pursue your vision. They form your ethical compass, shaping your culture and guiding everyday behavior. Unlike goals or objectives, values don’t change quarterly—they are enduring principles that help align decisions and actions.
Examples might include:
- Integrity and transparency
- Innovation and continuous learning
- Customer-centricity
- Excellence and ownership
Your values should influence hiring, strategy, communication, and even partnerships. When values are deeply embedded, they create consistency across your organization—even during times of uncertainty or change.
To implement values effectively:
- Involve your team in defining them.
- Embed them into onboarding and training.
- Celebrate behaviors that reflect your values.
Organizations that live their values consistently outperform those that treat them as mere slogans.
3. Identify Focus Areas
Focus areas are strategic themes or priorities that sit between your vision and your objectives. They represent the pillars of your strategy—areas where you need to concentrate your time, resources, and energy.
Typical focus areas include:
- Product development
- Market expansion
- Customer experience
- Operational efficiency
- Brand awareness
- People & culture
Your focus areas should reflect what matters most over the next 6–12 months. Too many priorities dilute attention; too few might miss critical dimensions.
Limiting your focus areas to three to five is ideal. This balance ensures you cover core strategic domains without overwhelming your team. Review and revise focus areas quarterly to stay aligned with market and business changes.
4. Translate Focus Areas into Objectives
Within each focus area, you define objectives—clear, measurable outcomes you want to achieve. Objectives break down your strategic priorities into actionable targets.
Use the SMART framework to ensure objectives are:
- Specific: clearly defined
- Measurable: tied to metrics
- Achievable: realistic and resourced
- Relevant: aligned with your focus areas
- Time-bound: deadline-driven
For each focus area, aim for three to five objectives. This provides enough direction without overwhelming your team or losing focus.
Example:
- Focus Area: Customer Retention
- Objective: Increase monthly retention rate from 78% to 85% by Q4
Make sure objectives are outcome-based, not task-based. “Increase MRR by 20%” is stronger than “Launch new pricing page,” because it focuses on impact rather than activity.
Source: Doran, G. T. (1981). There's a S.M.A.R.T. way to write management's goals and objectives. Management Review, 70(11), 35–36.
5. Measure with KPIs and Drive with Actions
Objectives guide you, but KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) and actions move you forward.
- KPIs show whether you’re on track by measuring performance against each objective.
- Actions are the specific steps your team will take to achieve the objectives.
Example:
- Objective: Increase monthly retention rate to 85%
- KPI: Monthly retention rate tracked via analytics
- Actions: Launch onboarding improvements, implement feedback surveys, set up re-engagement email flows
KPIs make progress visible and help inform timely decisions. Ideally, they should be updated frequently (weekly or biweekly) and reviewed in team meetings. Every KPI should be assigned to an owner.
Actions, on the other hand, are your execution playbook. Without action, even the best strategy will stagnate. Actions should be broken down into manageable tasks, prioritized, and tracked.
Source: Parmenter, D. (2015). Key Performance Indicators: Developing, Implementing, and Using Winning KPIs. Wiley.
6. Ensure Alignment and Accountability
The strength of the Cascade Model lies in its ability to align everyone—from executives to individual contributors—around shared priorities. When implemented well:
- Everyone understands how their work supports the bigger picture.
- Teams stay focused on what matters most.
- Progress becomes measurable and transparent.
Alignment increases ownership, reduces redundancy, and accelerates execution. It creates a shared language across departments and ensures that everyone rows in the same direction.
To ensure alignment:
- Communicate the strategy regularly.
- Use tools like dashboards or visual scorecards.
- Hold structured check-ins to track execution and identify blockers.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Even strong strategic models can fall apart in execution. Watch out for these mistakes:
- Setting too many focus areas or objectives: This spreads teams thin and leads to confusion.
- Defining vague or immeasurable KPIs: You can’t improve what you can’t measure.
- Failing to assign ownership to actions: Without clear accountability, execution slows.
- Neglecting regular reviews: Strategy must be dynamic, not static. Adjust when needed.
Mitigate these risks by building review cadences into your process. Quarterly strategy sessions, monthly KPI reviews, and weekly action check-ins can help keep things on track.
Final Thoughts
Strategy isn’t something you create once a year—it’s an ongoing cycle of prioritizing, executing, learning, and adjusting. The Cascade Model transforms strategy into a living, breathing system that evolves with your business.
Whether you're running a startup, scaling a team, or leading transformation in a larger organization, this model offers structure without rigidity. It gives you a framework to keep moving—even when circumstances shift.
The key takeaway? Strategy lives or dies in execution. And execution thrives with clarity, focus, and accountability.
Need help applying this framework to your own business or team?Let’s work together. Check out my profile on MentorCruise: mentorcruise.com/mentor/jimmyjaspers and book a session.
Disclaimer: This article is written in a personal capacity from my role as a mentor and entrepreneur.