If you're a beginner and want to have a tech career, you might be confused about all the career specialization choices. There are things like Machine Learning/AI, Data Science, Game Development, Quality Assurance, Cyber Security and of course, Web Development.
If you have already made up your mind and you have your reasons to choose a certain career path (excluding Web Dev), then, this post is not for you. Otherwise, I will try to convince you why you should start with Web Development as the first step:
It has a high demand in the job market
Web is the most accessible platform, anyone from anywhere can access it. All they need is an internet connection and a device capable of handling a web browser. If you make an Android app, it will be only runnable on Android devices. But if you make a Web app, everyone can use it
No matter what you choose as a tech career, you will be directly or indirectly involved with web development. Even if you're an AI Engineer/Machine Learning Engineer, still you would need basic knowledge of Web Development. So, learning Web Dev is not a bad investment in any scenario, even if you switch to Data Science or AI.
Ever used Uber? Of course you did (or at least some similar service). What does it do? It gives a ride-sharing platform and nothing more. Although the app seems very nice, it's actually the backend code that's doing all the magic, which also falls under the web category. They even have a dedicated Research and Development team called Uber Engineering where they get millions of investments and they're constantly bringing revolutionary changes in Software Engineering. Most of the work they do there is related to making the 'ride sharing' platform better, which might have seemed 'simple' to you a few minutes earlier. Interesting, right? You might store some data in a database, do some CRUD (No worries if you don't know the term) operations and make a nice looking web page. But you will be stuck when you're given a complicated system like Uber, which is running at a large scale and millions of users are using it at once.
The gist is, web development can be very challenging and interesting work. But to face those challenges, you need to get a job as an engineer. So, let's guide you on that path. I am a Software Engineer working with web-based SaaS product, so I think my knowledge is valid enough for you.
Originally inspired by the well known Developer Roadmaps, I shall share a mini roadmap with narrowed down choices (so that it's much easier for you to decide), my own experience and my learning resources so that you don't have to waste time to compile these things and look into the vastness of resources with great confusion.
Why follow my choices? Well, the technologies I listed here are widely popular and has a high demand. If you can grasp the whole roadmap, you would have the capability to tackle any other technology in future if required.
But before doing that, let's get familiar with some job titles that relate to web development:
Frontend Engineer (Client-side)
- Turn web design (provided by UI designer) into code.
- Implement user interactions like button events, visual feedbacks etc.
- Implement data model and data state. Decide how data is going to be stored and manipulated throughout the application
Backend Engineer (Server-side)
- Design and implement database schema
- Take system architectural decisions. Decide how to scale up your application to thousands or millions of users
- Implement business logic for your unique product (like what happens on the server-side when a customer requests a ride in Uber)
- Use tools and technologies to provide data insights
DevOps Engineer
- Bridges the gap between Developers (who write code) and the Operations (who run the code) team. In simple terms, a backend/frontend engineer writes the code, while the DevOps engineers main responsibility is to serve the written code to customers
- Automates the deployment pipeline using CI/CD (Continuous Integration and Deployment). By deployment, I mean from writing the code to serving it to end customers (SDLC).
- Manage the servers and network. Ensure systems are running properly without downtime
- Not directly involved with the implementation of the product
Full-Stack Software Engineer
- Works in both Frontend and Backend
- In most companies, the title is generally 'Software Engineer'
- Small to moderate companies offer full-stack roles. For bigger companies, the product is so complex that a full-stack role is not possible. In those cases, they offer specific Backend or Frontend positions
Site Reliability Engineer (SRE)
- Engineers who solve operational/scale/reliability problems and maintain infrastructure
- It's an overlap of DevOps and Backend Engineering, or we can say a glorified form of DevOps Engineering
- Has somewhat involvement with the software product by providing reliability consultations (like what DB to use or not to use, how to scale properly etc)
- Not really involved in writing code for the actual software, rather routine maintenance work
Please note, based on your company, you might be simply called a Software Engineer regardless of which above category you fall into.
In this article, I will guide you to the barebones, which is Frontend and Backend. These guidelines will be a starting point. I will also link a post of mine where you can get an idea of DevOps. There is no different career path for SRE. Just learn Backend Engineering and DevOps properly, that's it.
The Roadmap
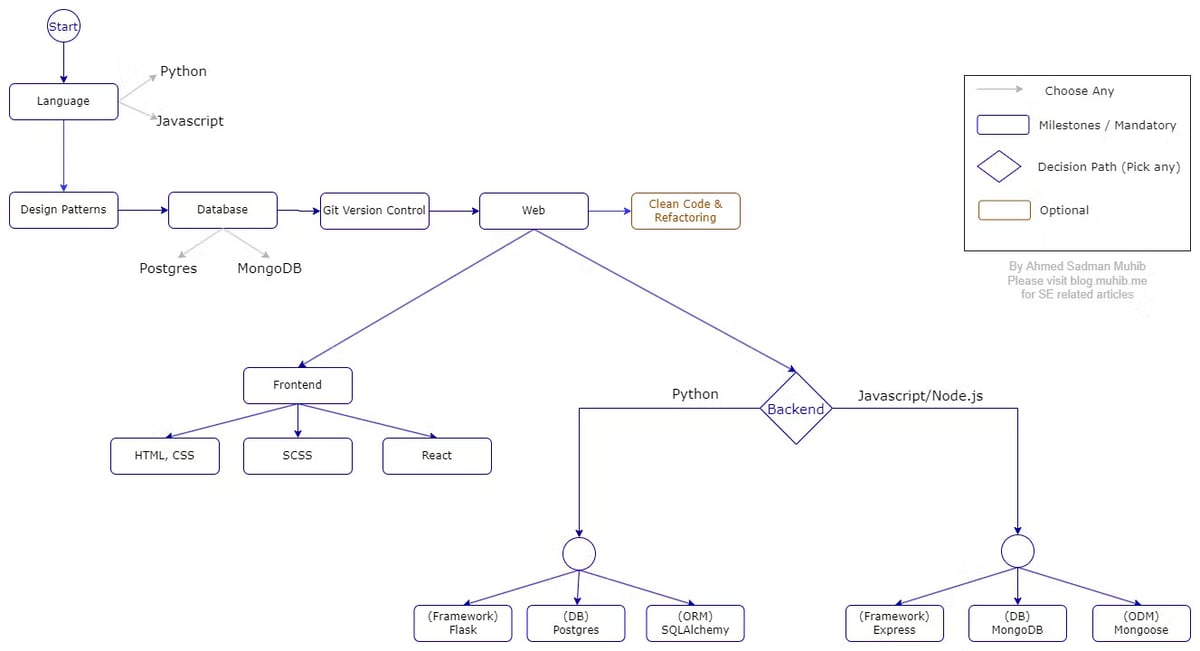
If the rendering of the image is unclear, please use this direct link of the Roadmap. Please go through the roadmap carefully as we will be referencing this for the rest of the article. Estimated time duration to complete the roadmap following only one Backend path would be around 6-8 months. Also, this is the barebones of web development and there are a lot of things that you will have to learn later. But for now, this roadmap is perfect for beginners.
Pick a Programming Language
This is the first step. As I have listed, my preferred choices are Python and Javascript. These two are very promising languages and they are never going to go away. Let me share the benefits of picking either of these languages
Python
- It's easier to learn, difficult to master. It looks like almost natural language
- Has powerful and battle-tested (read 'mature') web tools and frameworks
- Great community
- If you're thinking of switching to Machine Learning, AI or Data Science later, go blindly with Python. Because literally speaking, Python is the 'heart' of those sectors
Javascript
- The most popular and loved language
- Great community
This is the language with diverse possibilities. If you learn this language, you can do Web Frontend, Server programming (backend), cross-platform mobile app development, desktop app development, game development and even for Machine Learning (experimental) and Embedded Systems programming. Although, I would not recommend this language for the last two. But you can see the picture, this language has the most diverse amount of use cases.
Jeff Atwood, one of the founders of the life-saving platform (for devs) Stack Overflow, said this back in 2007
Any application that can be written in JavaScript, will eventually be written in JavaScript. - Jeff Atwood
Popularly known as Atwood's Law, this is totally true nowadays. Recently, Google released zx, which is a JS scripting library that might have the capability of replacing Bash/Shell scripting in future (just my personal opinion, but it's very promising though).
So make a decision and pick one language. Both of them is fine. Remember, which language you pick will affect your choice for the Backend section. Eventually, you should target to cover the whole roadmap, not just a specific path. So, look into the benefits and decide which language suits you better and start learning.
Okay, if you still can't decide, go with JavaScript.
You might have heard of Node.js, it's a programming language. It's identical to JavaScript, with absolutely zero difference. It is given a different name because it can run outside a web browser environment, unlike JavaScript.
Learning resources are provided at the end of the article
Design Patterns
Design patterns are typical solutions to common problems in software design. Each pattern is like a blueprint that you can customize to solve a particular design problem in your code
Design Patterns are the most valuable but most underestimated skill. It relates to how you should structure your code in an Object-Oriented Design environment. In some cases, you will not be using these pre-defined patterns directly. But these are required so that you understand common OOP principles and even use customized versions of these patterns when you're working with large codebases.
Unless you have a thirst for learning, you don't need to go through all the patterns. Just focus on those listed below:
Creational Patterns: Factory, Abstract Factory, Singleton, Builder
Structural Patterns: Adapter, Decorator, Facade
Behavioral Pattern: Command, Observer, Visitor
Don't know what Object Oriented Programming is? no worries, follow the roadmap and it will come on its own accord
Database
Databases are used to store information. There are many diverse database choices. Mainly divided into SQL and No-SQL categories. I have made the choice easier for you. You're a new learner. So, it doesn't matter which database you choose to learn first. In an ideal scenario, you should learn both MongoDB and Postgres (at least at some point in future).
You need to be fluent with at least one database technology before jumping into web dev. If you previously chose the Python language, take Postgres (SQL). Otherwise, MongoDB (No-SQL database). Just so you know, you can use SQL databases with JavaScript too. I just recommend MongoDB because its syntax and usage matches JavaScript. Also, most JS-based web dev tutorials cover MongoDB by default. Although relatively new, MongoDB is being widely adopted by many companies. It can overcome many design limitations of a traditional SQL database. But don't think one is superior to another. Both have their own advantages and disadvantages.
Version Control with Git and GitHub
Any software is subject to change, it can change daily, or even hourly. This is why Software Engineering exists in the first place. Version control systems like Git and GitHub are tools that allow you to record changes in your codebase and revert to a previous point if something fails. Also, it gives you the necessary tools to collaborate with other developers. It's a must-have knowledge no matter which tech sector you work in.
Frontend
You have to start with Frontend first. You have to learn HTML, CSS, SCSS (CSS on steroids) and React. React is a front-end framework that makes front-end development much easier. There are also other frontend frameworks, but learning React is the best choice as it has the best features of the bunch and also high demand in the job market.
Backend
Now you have to choose either of the paths. The choice should depend on what you picked in the Language section. We will be focusing on how to build REST APIs because this convention is widely used in every type of mobile or web applications you see around you. All the provided tutorials for the backend has REST APIs covered.
Python Path
Flask is a Python-based framework to write web applications using the Python language. It's easy to learn and very extendable. There's another framework named Django. But Django automates a lot of stuff. Personally, I don't prefer Django. On the other hand, Flask gives you a lot of control. Starting a project with Flask is much easier compared to Django. As Flask gives you much control, you will be able to learn a lot of things because those will be implemented by your own hand
As for database choice, there is only Postgres. Please note, you can use any database with Python. Not just Python, you can use ANY DATABASE with ANY LANGUAGE. But in this path, I have selected Postgres. Later when you master the whole roadmap, you can also use MongoDB with Flask if you want
ORM (Object Relational Mapping): ORM is an abstraction layer that sits on top of the database. Using ORM, you can use the programming language's own feature to manipulate and access data, instead of using a query language like SQL.
Let's say you want to select all students from the student table whose age is greater than 18. Also, assume you're using MySQL database. But before fetching the data, let's create a table where the data will be stored. We have to use SQL to issue the commands
<pre><code>CREATE TABLE students (
id INT PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(50),
age INT
);Running this SQL will create a table. Now to store some data:
<pre><code>INSERT INTO students VALUES (1, 'John', 17);
INSERT INTO students VALUES (1, 'Doe', 19);Now, to fetch the students whose age is greater than 18
<pre><code>SELECT * from students WHERE age > 18;The above is a MySQL specific database query. SQL is quite similar to natural language. The given query will return all students having age greater than 18.
Now, if you use ORM with your Python application, you don't need to know the SQL at all. Instead, you will do something like this to create a table (Python example):
<pre><code>class Student:
id = db.Column(...)
name = db.Column(...)
age = db.Column(...)The above is a class, which you will learn during your OOP portion of your selected language.
Inserting records
<pre><code>student = Student('John', 18); # id will be calculated automatically
student.save()To get all students whose age is greater than 18
<pre><code>Student.query.filter_by(age > 18).all()As you can see, ORM allows you to use Python syntax to query and manipulate the database. You don't even need to know SQL (although you have to because otherwise, you won't know how to use ORM efficiently).
More importantly, using ORM saves you from a lot of troubles, for example, it prevents SQL injection which is a hacking method. Also, you can switch to any SQL database at a later point. For example, let's say we're using MySQL. Later if we want to switch to Postgres, we don't have to change the above code at all. How does ORM do that? Well, it's just an abstraction. Based on which database engine you're using, it can generate the equivalent dialect for you. So, the ORM will convert the Python statement Student.query.filter_by(age > 18).all() into
<pre><code>SELECT * FROM students WHERE age > 18;Not only Python, but every language also offers some kind of ORM to work with. For Python, the most popular one is SQLAlchemy. You will have to learn that.
Node.js Path
Don't worry about the title, JavaScript and Node.js both are the same as I stated earlier. For server programming, you will have to get out of the browser environment thus calling it Node.js seems appropriate here. In this path, the web framework is Express, the database is MongoDB. MongoDB is a No-SQL database that is quite different from a SQL database. At some point in future, you should know both MongoDB and Postgres.
The ODM (Object Document Mapping) is Mongoose. ODM and ORM are the same things. But as this is a No-SQL database, there are some changes in the terms and definitions
Clean code and refactoring (Optional)
For the curious-minded people out there. This will definitely help when you start your first job. You can go through this much later if you want. Clean code and refactoring is a skill that comes through experience. But still, you have to know some concepts so that you get directed to the right path.
Resources
The section you've been waiting for! Here, most of the resources I share were used for my own learning. For some parts, you have to follow multiple tutorials. Please note, order matters in those cases.
Many Udemy resources are paid. Although pirated contents are available, you are encouraged to spend on the courses because it's worth investing in. So, here we go:
Language
Python
JavaScript
The Complete Javascript course by Jonas
Please note, this will also include some basic HTML, CSS. To learn JavaScript, there is no way to avoid HTML, CSS. But no worries, the instructor will guide you through smoothly.
Clean Code and Refactoring
Design Patterns
Refactoring.guru: Design Patterns
Database
Postgres
MySQL and Postgres are quite the same in syntax, only the engine is different. There's no good tutorial for Postgres in my knowledge so follow the MySQL one.
MongoDB
MongoDB - The Complete Guide by Academind
Git and GitHub (Version Control)
As you can see, there are multiple resources. You have to go through all of them, in order. Don't worry, these courses are very small. It would take you at most 1 week to master the basics.
Frontend
HTML, CSS, SCSS
React
React 16: The Complete Guide by Academind
Things like Redux, Redux Thunk are obsolete nowadays. It's also difficult to understand. React has introduced 'Context API' which works as a replacement for Redux. So, you can safely skip or skim through the Redux related sections.
Backend
Python Path
- Build REST APIs with Flask (Very average tutorial, misses a lot of things. But still a bit better than others. You have to follow it because it shows some modern techniques)
- Flask Mega tutorial by Miguel Grinberg (Read the whole series. This will be the series that you will take as reference point while writing Flask code. Forget the bad practices introduced to you in the previous tutorial)
Just a reminder, where you see these numbered tutorials, you have to follow all of them, in order. These are not options, but mandatory.
Node.js Path
The given tutorials cover everything from the roadmap.
Where to go from here
Now you have a solid basic understanding to create robust Web solutions. Soon, I will release another article with a roadmap of advanced topics. Stay tuned! For now, you can look into the Cloud section. I have a great starting point I've provided in my blog titled Cloud Deployment for absolute beginners.
Some tips for new learners
- Don't rush. Take your time to learn these things. Learn everything thoroughly
- Do Projects. This is extremely important. Don't fall into the learning loop. Be ready to get your hands dirty as soon as possible
- Every project you do, keep it in GitHub. This is extremely important
- Try to get involved in open-source contributions . It will drastically boost your profile
- Don't forget that Data Structures and Algorithms are important and might be asked in company interviews. This is not a Computer Science roadmap, so discussing algorithms is out of scope. But you should have a basic understanding. You can use Leetcode (Easy + Medium levels) to practice interview questions.
- Don't waste time on Coursera certificates. Instead, invest time in doing projects. By far, I haven't seen any company that judges a candidate by their Coursera certificates. I'm discouraging this because most people try to gather as much certificate as possible, without learning anything valuable. Even for a beginner, a company will look into how much real experience you have building things and solving problems, not those fancy certificates you showcase on Linkedin.
- It's much better to pick few things and master them instead of being a jack of all trades
- There is no universal tech stack that can get you a job in any company. When hiring beginners, most good companies are tech agnostic
- Even if you don't know a tech stack, you can learn that easily because now you have a strong fundament
Speaking of career in web dev, a mentor can help you in many ways. Having a mentor will boost your learning speed, help to have a clear understanding of the concepts and guide you through constant improvements. In our research at a coding bootcamp, we saw that having 1-1 mentorship increases the chance of a successful career by almost 200%. I'm mentoring developers on MentorCruise. Don't forget to check it out.
Thank you for reading this far. If you have any questions or feedback, please don't hesitate to drop a comment. This will encourage me a lot.
If you liked this article, please share it with your circle. Also, don't forget to follow my blog. Have a nice day!